Commonhold – a panel discussion
Commonhold – a panel discussion
Below is a note if some of the key points from the panel debate at the ARMA Conference 2017
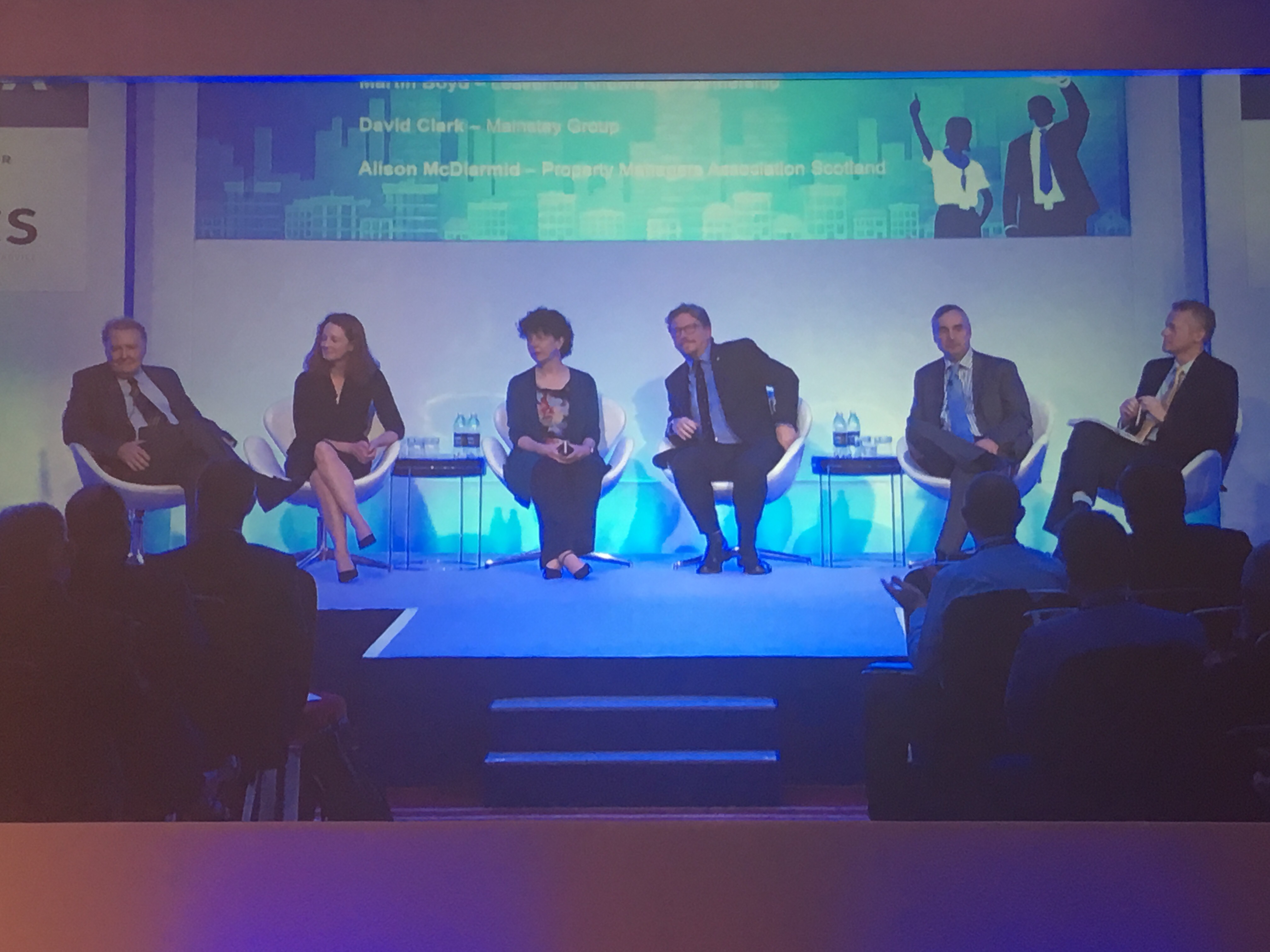
The panel comprised 5 industry experts and looked at a number of issues. Appearing on the panel were; Philip Rainey QC, Professor James Driscoll, Jennifer Bourne of U.K.Finance (formerly the CML), Martin Boyd of the Leasehold Knowledge Partnership (LKP), David Clark of the Mainstay Group and Alison McDiarmid of the Property Managers Association Scotland.
The broad conclusion was that Commonhold was a good thing and that its introduction couldn't come soon enough! (I know that this is not a view that everyone will share).
Some of the key points are picked out below:
The lenders' concern – redevelopment
Under Commonhold if 75% of the unit owners vote in favour, then the building can be re-developed. This would mean that the property interests would come to an end. The position of a secured lender with a mortgage over a unit is not clear.
If they aren't in favour of the same and / or fear a shortfall for instance, how will they be protected?
Jennifer Bourne of U.K. Finance expressed concern on this.
Valuation issues – a two-tier market?
Another concern – which would be more of an issue perhaps for existing leaseholders, would be what if suddenly Commonhold units have more value (or conversely less) than leaseholds?
Why or how would this happen? – I have commented before that if there were to be a sunset clause on leasehold then at some point investors in ground rent might well 'pile in' to the remaining freehold reversions – and the price of these would be driven up. This would have a knock on effect on leaseholders who would have to pay more to enfranchise and as a result might if matters became extreme, have less valuable properties.
Not a problem for Commonhold itself, but something of the law of unintended consequences.
The Scottish position
Freehold in Scotland works for shared units like flats because there are no restrictions on passing on positive covenants with a transfer of the land.
Would that be a solution here? Well, perhaps up to a point, but the Scottish take on this is that the system is far from ideal, because in order to get major works etc. progressed, everyone has to agree and, we all know how difficult that can be.
This was the view of Alison Mc Diarmid of Property Managers Scotland who says that she would prefer Commonhold.
What about the position of investors? Is ground rent sometimes a good thing?
David Clark of the Mainstay Group commented that we need to keep ground rents reasonable but what about the needs of pension funds etc. depending on this income.
Whilst not immediately popular, ground rents at an acceptable level do provide a valuable source of fixed income. The impact of losing this should be assessed and there are numerous large funds that have invested in the sector.
How to make it happen?
What about changing the requirement for unanimity to get conversion to Commonhold?
This has been mooted before. As matters stand 100% of the flats would have to agree to be able to convert. That means only one person can block a conversion of they want to.
The threshold could be reduced, but this would also require lender consent.
James Driscoll commented that the threshold should be reduced. His view was that says long term it would be far better if we offered Commonhold as an alternative.
There are after all, 4m leaseholders – possibly 8m voters if the flats are co-owned. They will all have something to say about these issues.
All in all there is lots to discuss if Commonhold is to become a reality and a key question will have to be how this issue can and will compete for the available parliamentary time.
Mark Chick
18.10.2017

 So what is the answer to the leasehold scandal? Is it commonhold? Or is it going to take a bit more for commonhold to take hold?
So what is the answer to the leasehold scandal? Is it commonhold? Or is it going to take a bit more for commonhold to take hold?